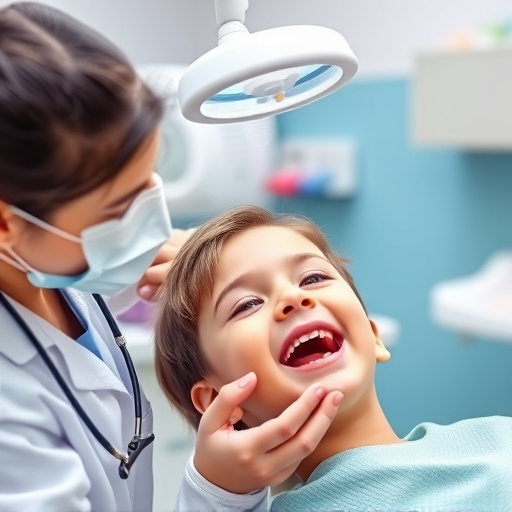
Severe gum infections (periodontal diseases) caused by plaque buildup lead to gingivitis and can progress to periodontitis, damaging tooth-supporting structures and causing tooth loss. Linked to systemic conditions like cardiovascular disease and diabetes, these infections require immediate attention. Antibiotic therapy treatment stabilizes and heals infections by targeting bacteria, reducing inflammation and bone loss. Combined with regular dental cleanings, check-ups, brushing, flossing, and surgical interventions when necessary, antibiotic therapy offers a comprehensive solution for long-term oral health.
Severe gum infections, or periodontitis, can be a debilitating condition, affecting not just oral health but overall well-being. This article delves into understanding the causes and impact of such infections, highlighting how they can destabilize oral health and lead to systemic issues. We explore the role of antibiotic therapy treatment as a potent solution for stabilization, discussing its mechanisms, benefits, and why it’s crucial in managing and preventing severe gum infections.
- Understanding Severe Gum Infections: Causes and Impact
- Antibiotic Therapy Treatment: How It Works and Its Benefits
- Effective Management and Prevention Strategies for Severe Gum Infections
Understanding Severe Gum Infections: Causes and Impact

Severe gum infections, also known as periodontal diseases, are a common yet serious oral health issue that requires prompt attention. These infections can have diverse causes, often stemming from a buildup of plaque and bacteria along the gum line. Initially, they may present as gingivitis, characterized by redness, swelling, and bleeding gums. If left untreated, gingivitis can progress to periodontitis, which is a more severe form affecting the structures that support teeth, including bones and ligaments.
The impact of severe gum infections extends beyond mere discomfort. They can cause significant damage to oral health, leading to tooth loss if not treated effectively. Moreover, research has linked periodontal diseases to various systemic conditions such as cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and respiratory issues. Therefore, seeking appropriate treatment is crucial, with antibiotic therapy treatment playing a pivotal role in stabilizing and healing severe gum infections, often as part of comprehensive dental care provided by family dentistry professionals.
Antibiotic Therapy Treatment: How It Works and Its Benefits

Antibiotic therapy treatment is a highly effective approach to managing severe gum infections, often requiring prompt intervention. When bacteria invade the gums, they can cause inflammation, pain, and even bone loss if left untreated. This therapy involves the administration of specific antibiotics targeted at eliminating the bacterial presence in the oral cavity. The medication works by penetrating the affected areas, killing the bacteria, and reducing the risk of further infection.
One of the key benefits of antibiotic therapy is its ability to prevent the escalation of gum disease from mild inflammation to more severe conditions like periodontitis. It can also aid in the healing process, promoting tissue regeneration and reducing the need for drastic measures such as emergency dental care or tooth extractions. By addressing the root cause of the infection, this treatment offers a long-lasting solution, contributing to overall oral health and potentially saving patients from future complications.
Effective Management and Prevention Strategies for Severe Gum Infections

Effective management and prevention are key when it comes to severe gum infections. Antibiotic therapy treatment plays a pivotal role in stabilizing these conditions by targeting the bacterial cause. Beyond this, several strategies can help prevent such infections from occurring or worsening. Regular dental cleanings and check-ups are essential to remove plaque buildup, which is a major contributor to periodontal disease. Early detection through routine care allows for less invasive treatments compared to advanced stages where tooth extractions might become necessary.
Additionally, maintaining good oral hygiene at home is crucial. This includes brushing twice daily with fluoride toothpaste and flossing once per day to control the growth of bacteria. In cases where severe gum disease has already developed, surgical interventions may be required alongside antibiotic therapy treatment to clean deep pockets around teeth and promote tissue regeneration.
Severe gum infections can significantly impact overall health, but with proper management, these conditions can be stabilized effectively. Antibiotic therapy treatment plays a crucial role in combating such infections by eliminating harmful bacteria and promoting tissue healing. By understanding the causes and implementing effective prevention strategies alongside antibiotic therapy, individuals can maintain healthier gums and avoid severe complications. This comprehensive approach ensures better oral health and overall well-being.