Antibiotic therapy treatment is a critical tool for combating bacterial infections, especially in dental practices. Prescribed to kill or inhibit bacteria growth, it aids in healing infections, supporting tooth repair, and preventing extensive procedures. The goal is to contain and eliminate infections, prioritizing individual and communal well-being through early intervention and preventive tactics. Efficient administration targets bacterial sources while routine oral exams and general dentistry form a strong defense against infection entry points, reducing community-wide outbreaks. Untreated infections can cause severe health complications; prompt antibiotic treatment targets and eradicates pathogens, minimizing future needs for intense therapy. Regular teeth cleaning significantly reduces potential pathogens, contributing to overall health.
Antibiotic therapy treatment is a critical approach to combat and prevent the spread of infections, playing a pivotal role in modern healthcare. This article delves into the fundamentals of antibiotic therapy, highlighting its basic concepts and key objectives. We explore prevention strategies aimed at curbing infection transmission and discuss effective measures for successful treatment. By understanding these aspects, we can optimize antibiotic usage, ensuring their longevity as essential tools in our fight against infectious diseases.
- Understanding Antibiotic Therapy Basics
- Prevention Strategies: Key Objectives
- Treating Infections: Effective Measures
Understanding Antibiotic Therapy Basics
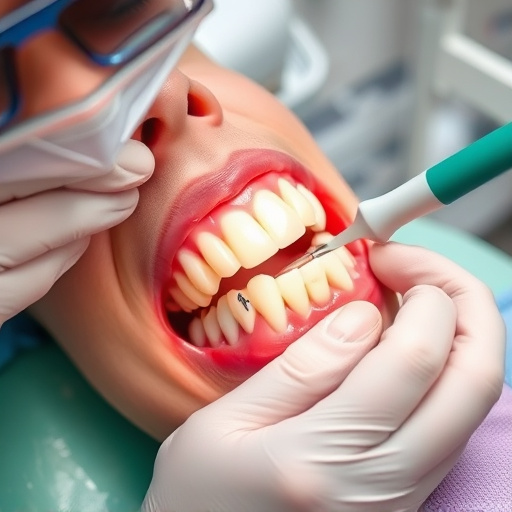
Antibiotic therapy treatment is a powerful tool used to combat bacterial infections and prevent their further spread. At its core, this type of therapy involves the administration of antibiotics, which are medications designed to kill or inhibit the growth of bacteria. Understanding how it works is essential in appreciating its role in maintaining good health, especially when it comes to general dentistry practices.
When a patient presents with an infection, whether it’s related to dental issues like tooth repair or more widespread conditions requiring dental fillings, antibiotics play a crucial part in treatment. Dentists often prescribe these medications to eradicate bacteria and reduce the risk of complications. By targeting and eliminating harmful microorganisms, antibiotic therapy can help heal infections, promote tooth repair, and even prevent the need for extensive dental procedures. This basic concept forms the foundation for effective infection control in both general dentistry settings and beyond.
Prevention Strategies: Key Objectives
The primary objective of antibiotic therapy treatment is to prevent the spread of infection and promote overall health. Key strategies focus on early intervention and robust prevention tactics. By administering antibiotics promptly, healthcare professionals can effectively combat bacterial infections before they escalate. This involves targeting both the source of the infection and potential reservoirs within the body.
In addition to direct therapeutic approaches, establishing a solid foundation through routine oral exams and general dentistry practices is vital. Regular check-ups enable early detection of dental implants or oral health issues that could serve as entry points for bacteria. Preventive measures such as these not only safeguard individual patients but also play a crucial role in mitigating community-wide infection outbreaks.
Treating Infections: Effective Measures
Antibiotic therapy treatment is a powerful tool in the fight against infections, and its primary aim is to prevent the further spread of harmful bacteria. When an infection is left untreated or improperly managed, it can quickly escalate, leading to more severe health complications. Effective measures involve promptly administering antibiotics to eradicate the specific pathogens causing the illness. This process disrupts the replication and growth of bacteria, halting their ability to multiply and spread within the body.
In addition to direct antibiotic treatment, preventive dentistry and general dentistry practices play a crucial role in infection control. Regular teeth cleaning and oral hygiene maintenance are essential aspects of keeping potential pathogens at bay. By removing plaque and bacteria from the mouth, these dental procedures contribute to overall health, reducing the risk of systemic infections that may require more intense antibiotic therapy treatment in the future.
Antibiotic therapy treatment plays a pivotal role in preventing infection spread by targeting both basic understanding and effective measures. By leveraging prevention strategies, we can achieve key objectives that underscore the significance of prompt and appropriate action. In treating infections, these therapies remain indispensable tools, emphasizing the need for informed application and responsible use to ensure their continued effectiveness.